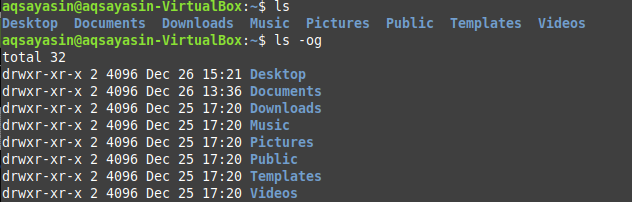
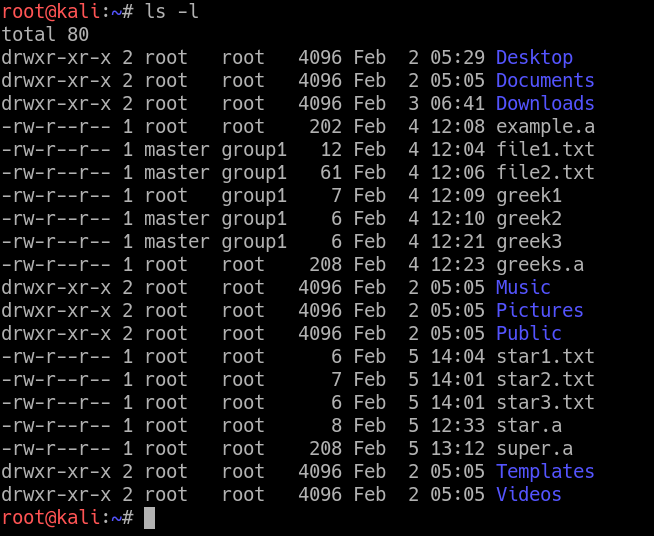
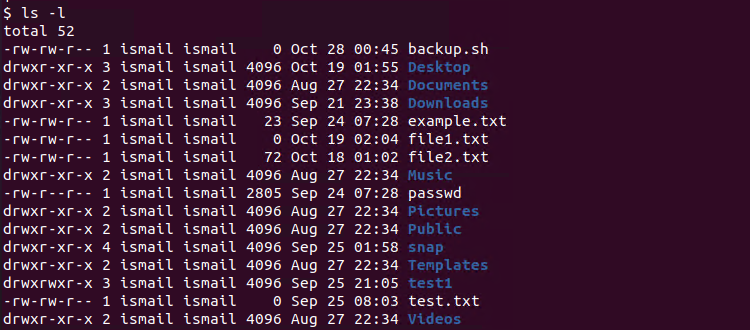
3 chmod examples Syntax and Options Related Commands chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners Let us understand CHMOD and CHOWN commands in detailLinux chmod Command Options Although not used very often, there are certain options associated with chmod, which are listed in the table below Option Descriptionc, changes Similar to verbose, but reports only when a change is madenopreserveroot Does not treat '/' specially (the default)
Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners
Chmod command in linux to change permissions
Chmod command in linux to change permissions- The chown command allows you to change the user and/or group ownership of a given file, directory, or symbolic link In Linux, all files are associated with an owner and a group and assigned with permission access rights for the file owner, the group members, and others chown master file1txt where the master is another user in the system Assume that if you are user named user1 and you want to change ownership to root (where your current directory is user1) use "sudo" before syntax



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
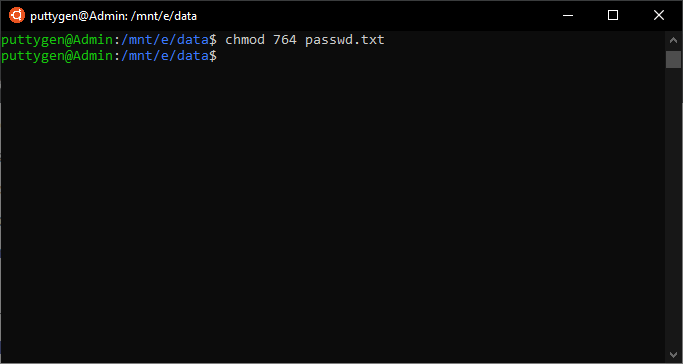
Sticky Bit Use the octal CHMOD Command chmod R 764 folder_name OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,gx,owx folder_name Linux and Unix operating systems provide the chmod command in order to change access permission for the files and folders The chmod command name comes from change mode The read, write, execute permissions with the stickyI have no idea how I could miss something so simple for so many years The more I learn the
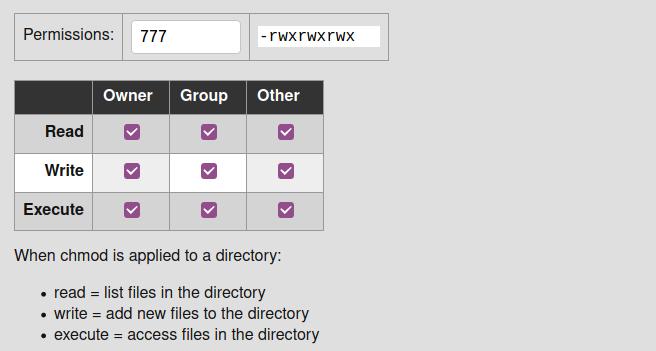
The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a fileChmod 775 Chmod 775 (chmod arwx,ow) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute (G)roup can read, can write and can execute (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute
What are file permissions and chmod command in Linux Chmod is an easy command in Linux However, it becomes difficult when you use all of its variations This command executes in so many ways Nevertheless, you need to know about file permissions File permissions decide whether a file is readable, writable, or bothIn Linux, the chmod commands are very helpful when you get stuck with the filesystem's permission As a Linux sysadmin, you need to know all the primary chmod commands on Linux In the entire post, I have described the most used Linux chmod command I have also shown how to save your system from the rookie mistakes of the chmod command Linux provides the chmod command which is used to change file and folder permission The chmod command is provided by all major Linux distributions like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Mint, Kali, RHEL, SUSE, etc The chmod command has different options and parameters but the chmod x is one of the most popular and used options for the chmod
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



1
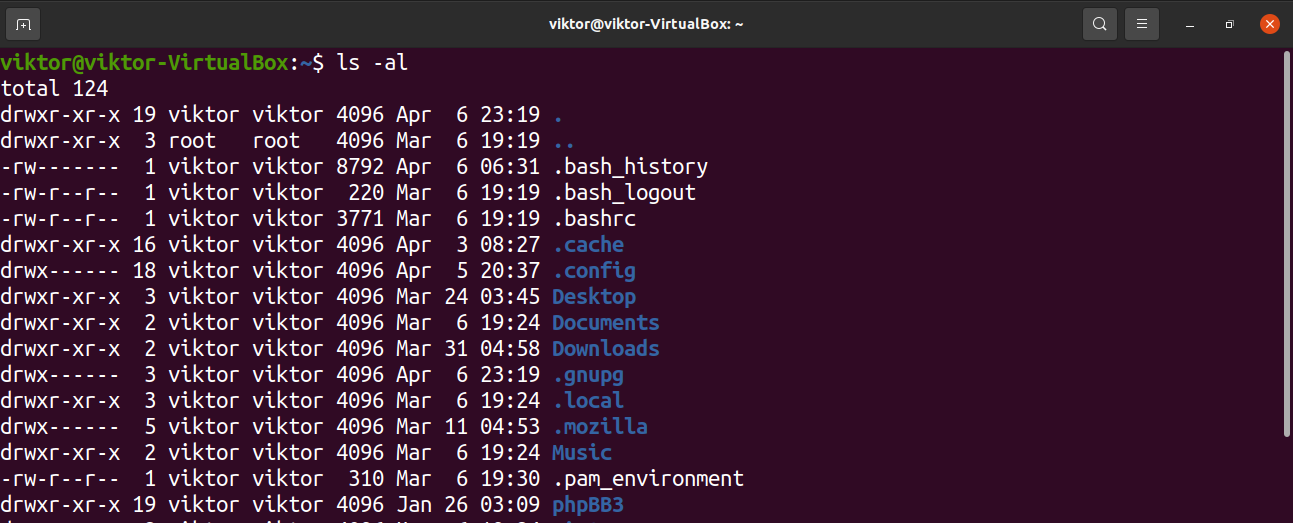
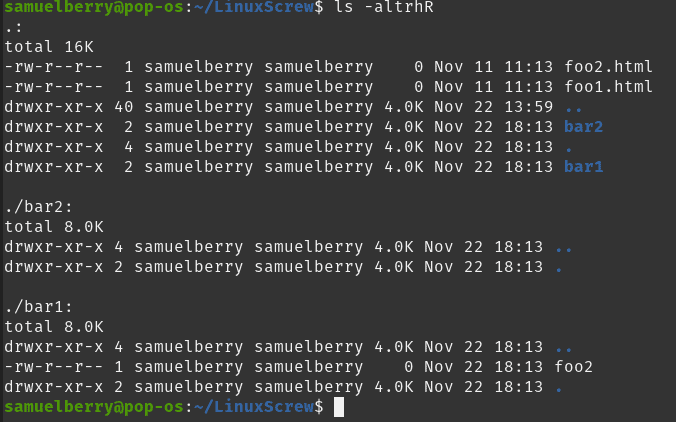
Linux commands chmod A quick guide to the `chmod` command, used to change the file mode Published Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions Read, write, execute Go into a folder, and run the ls al command The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linuxbased operating systems The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode The chown command stands for "change owner" is used to change the owner The subject of file permissions, and how to manipulate them with the chmod command, is a good place to start learning about these situations First, let's create a file and examine its long listing (In order to fit in the magazine, all the listings in this article are trimmed to fit) $ touch test_file $ ls l test_file rwrwr 1 eric users



Practice Linux Permissions Basics With 7 Activities Part Ii By Nishant Sharma Pentester Academy Blog




What Is Chmod X Command In Linux Linuxtect
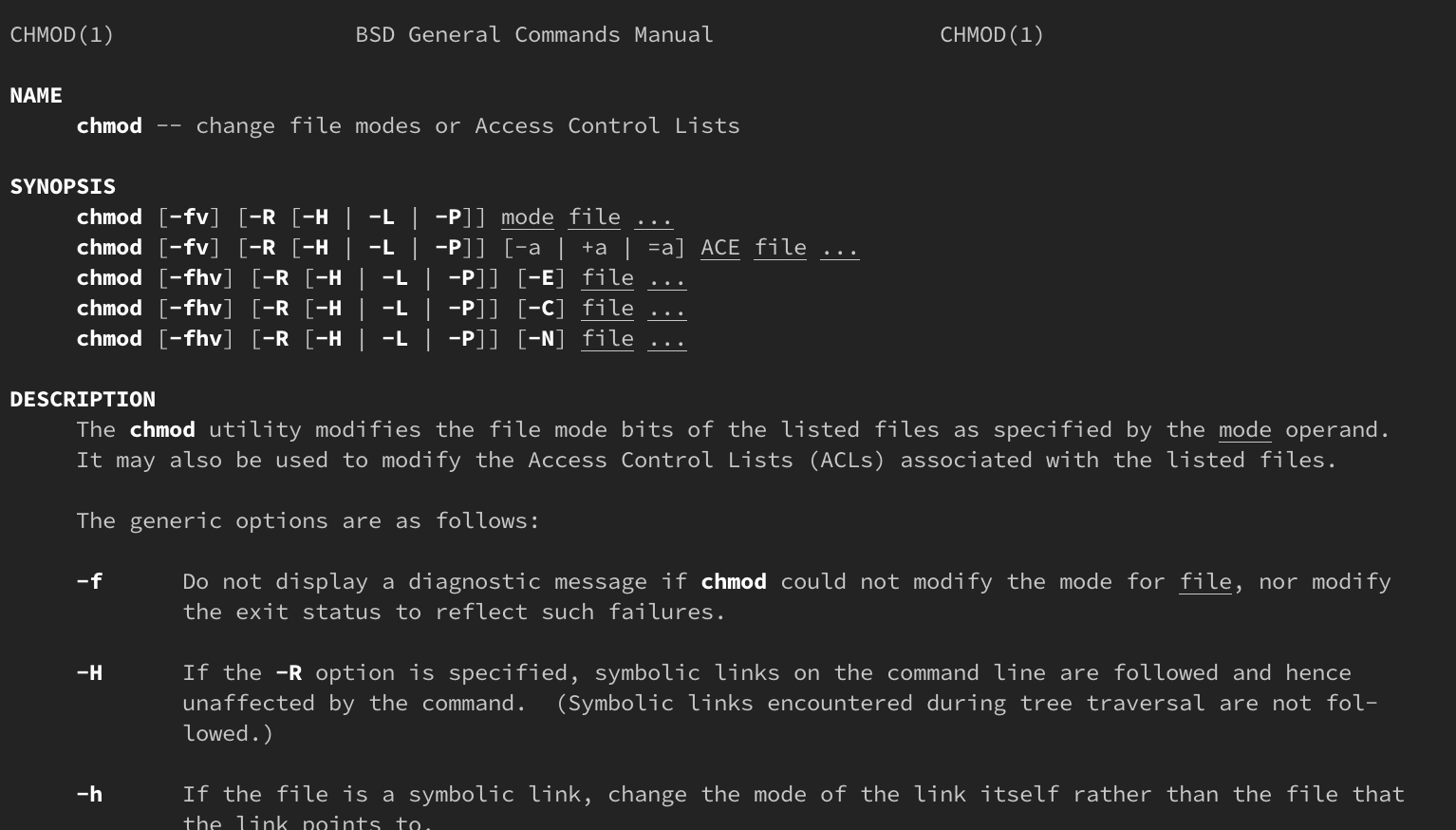
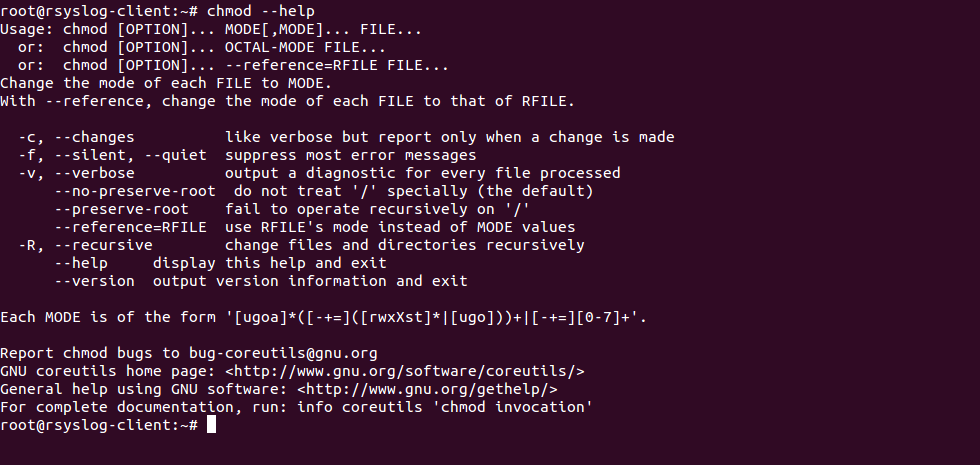
There are some details that you should keep in mind while using chmod with directories For all that info (as well as more details on chmod), head to the tool's man page About Himanshu Arora Himanshu Arora has been working on Linux since 07 He carries professional experience in system level programming, networking protocols, and command line Chmod Command in Linux (File Permissions) Written by Admin, Updated On chmod, terminal In Linux systems, the chmod command is used to change the permissions and access mode of files or directories This article The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article The command can accept one or more files and/or




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
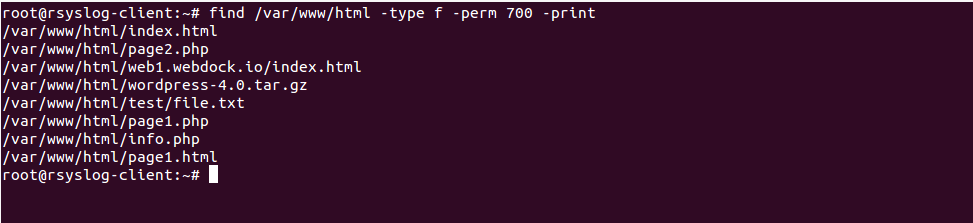
Linux Solution 1 chmod R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree You can use the find command C an you provide more information about chmod command octal mode number notation? In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change mode




File Chmod Gnu Png Wikipedia




Chmod Command Linuxhowto Net
chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions There are three sets of permissions One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file's group, and a final set for everyone else The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory They either permit, If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command It also allows to change the file permission recursively to configure multiple files and subdirectories using a single command In this tutorial, you will learn how to use chmod recursively and change file permission on Linux This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples



How Do Linux Permissions Work




Linux Permissions Posix Chmod Chown Chgrp Youtube
The command for changing directory permissions for group owners is similar, but add a "g" for group or "o" for users chmod gw filename chmod gwx filename chmod ow filename chmod orwx foldername To change directory permissions for everyone, use "u" for users, "g" for group, "o" for others, and "ugo" or "a Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls l command as shown below $ ls l samplesh rwxrwr 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 0312 sampleshLinux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)



Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights




How To Change Linux S Permissions Through A Practical Example Of The Chmod Command
I this video web will learn about file permissions in Linux We will talk about how chmod command can be used to change the file permissions File security a File Permissions and chmod Command in Linux In this article, we explain file permissions in Linux and one of the basic Linux commands for beginners, ie the chmod command used for this purpose, with its most frequently used command options Contents of The Article hideRunning openbox here but you can do this in just about any environment how you define the hotkey is gonna be specific to your window manager, though I have four Linux machines here to manage, this is what it looks like in ~/config/openbox/rcxml;




Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2 code factory chmod command in linux unix with examples chmod linux command chmod unix command linux and unix commands google youtube quora stackoverflow geeksforgeeks




How To Changes The Permissions Of A File Or Directory Studytonight



1
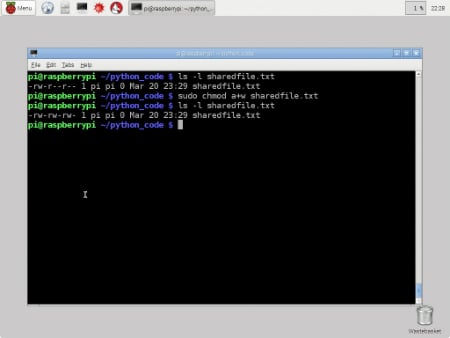
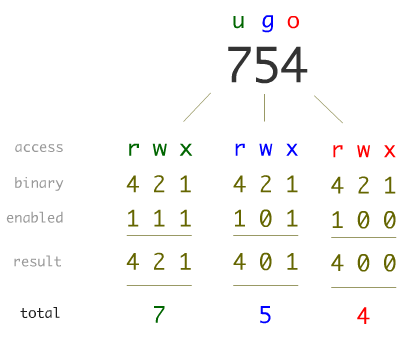
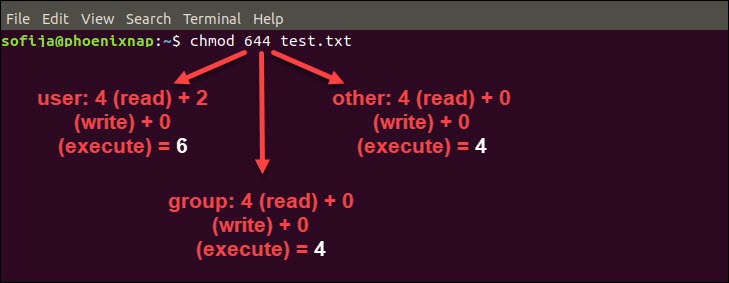
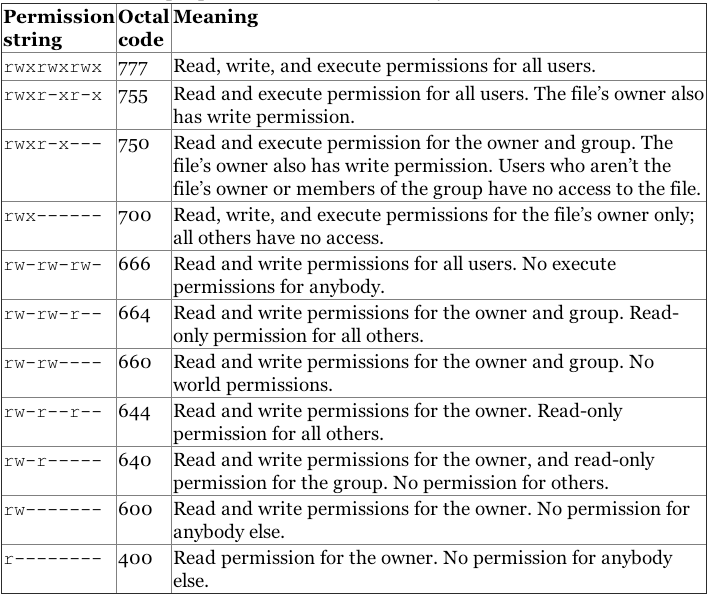
This manual page documents the GNU version of chmod chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits The format of a symbolic mode is ugoa = perms, where perms is either zero or more letters from the set How to Use chmod Command Let's say we want to change Linux file permissions from rwxrwrw to rwxr–r– Simply enter this line chmod 744 file name By executing this command, the owner can read, write, and execute the file ( rwx ) However, group and others are only allowed to read ( r– ) So Linux providing various kind of file permission that accessed by user or group For effective security Linux providing two authorization levels 1 Ownership 2 Permission If you like to generate permission quickly, Here you have Chmod Unix Permissions Calculator Using this you can generate your Octal or Symbolic value




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks
Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions It's usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux systemThis video explains chmod and chown commandspart 1 https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=kzRZVjHatuouser management in linuxhttps//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=iXU Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linuxbased distros




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft
This article explores chmod 777, a Linux command used to give ALL RIGHTS to the user, group, and others As a new Linux user, web developer, or system administrator, you have probably been instructed to type chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder into your Linux shell at some point Whenever you're running commands on your systems (especially as root!), you should In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command




Chmod Cheatsheet Linux




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up



Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies



Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
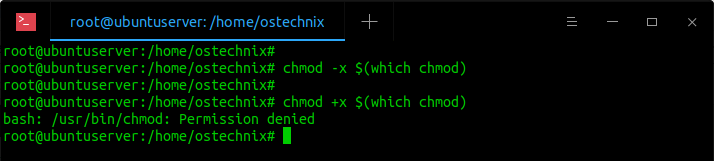



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
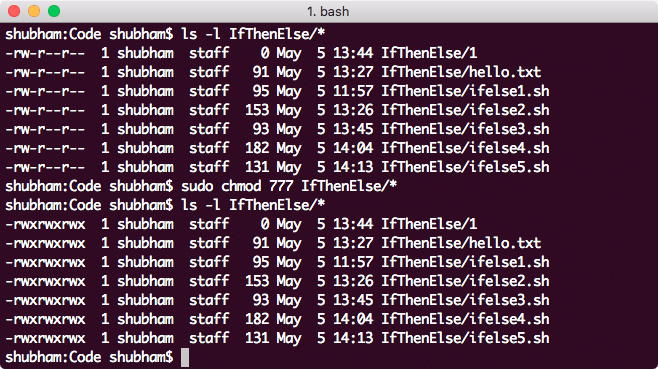



Linux Chmod Example
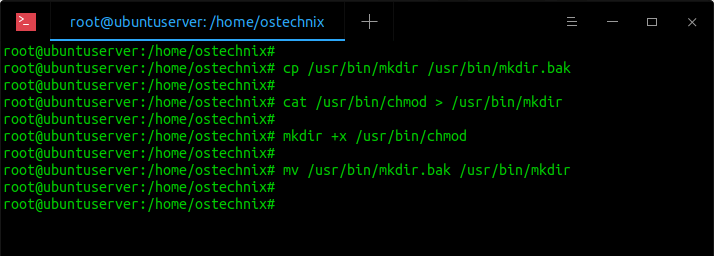



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners
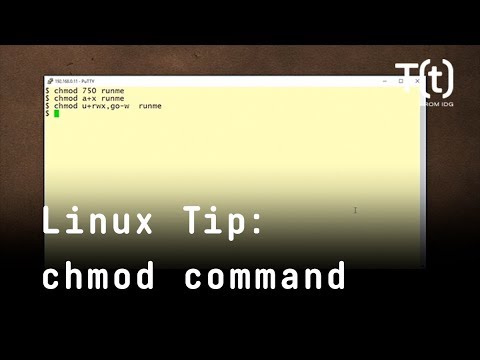



How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Youtube




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux Installmd
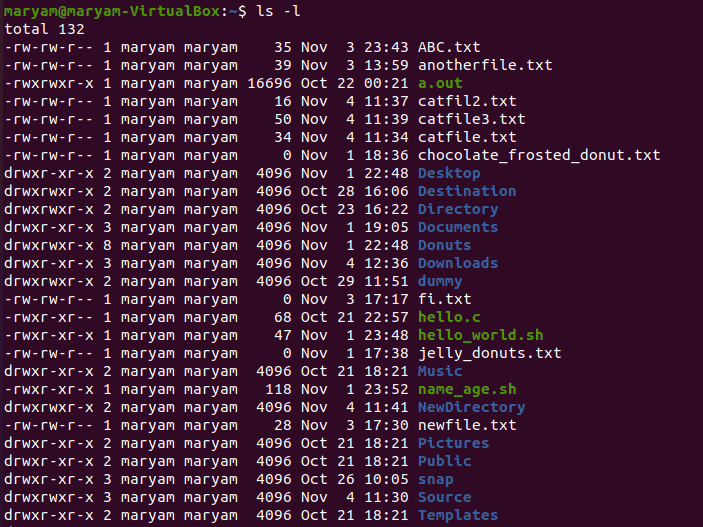



Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




Linux File Permission Javatpoint
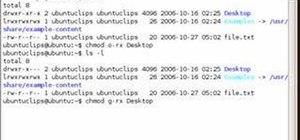



How To Use The Chmod Terminal Command In Ubuntu Linux Operating Systems Wonderhowto



3



Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples




Chmod Command In The Linux Unix Kodelazy




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub



Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc
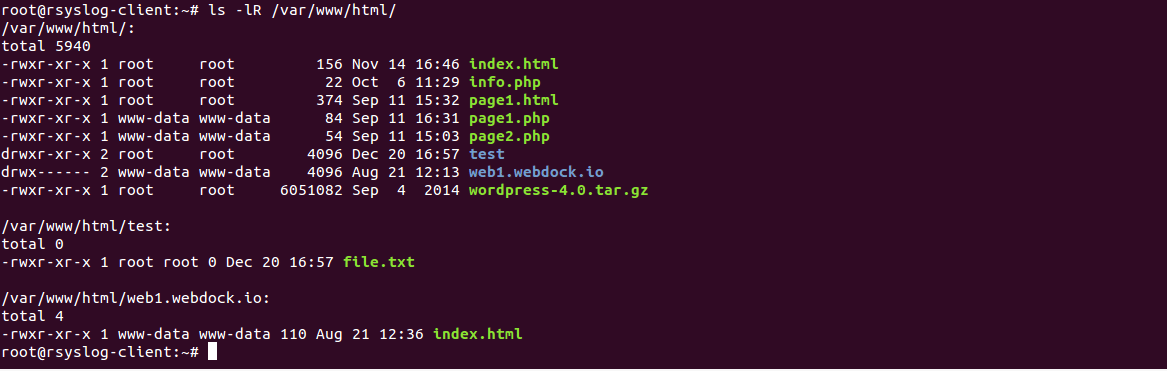



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com
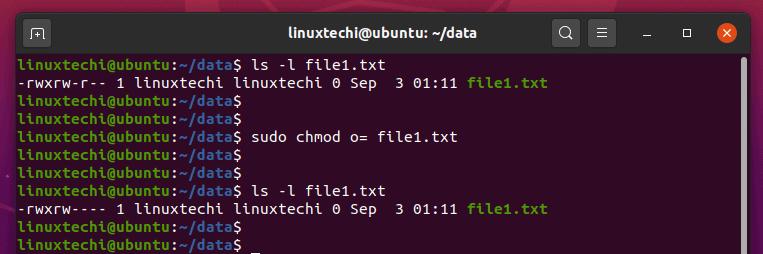



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
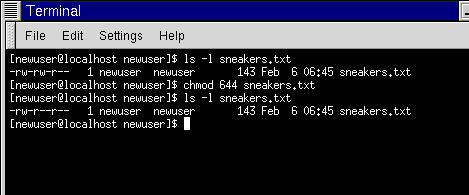



Fun With Numbers In Chmod




Travis Errors On Chmod Command After Generating New Beat Beats Discuss The Elastic Stack




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier



Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
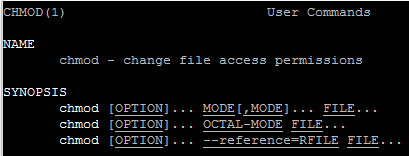



Chmod Command In Linux Alien Coders
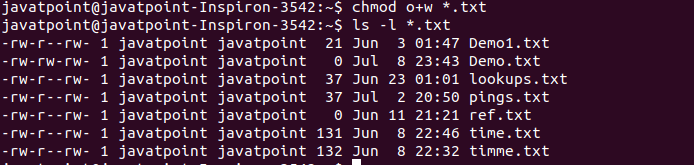



Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint




Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode




Why Isn T Chmod Command Functioning In Kali Linux Super User



Common Bash Commands




Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube




Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper




Linux Command 9 Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Linux From Beginning




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




How To Run Sh File In Linux How To Use Linux
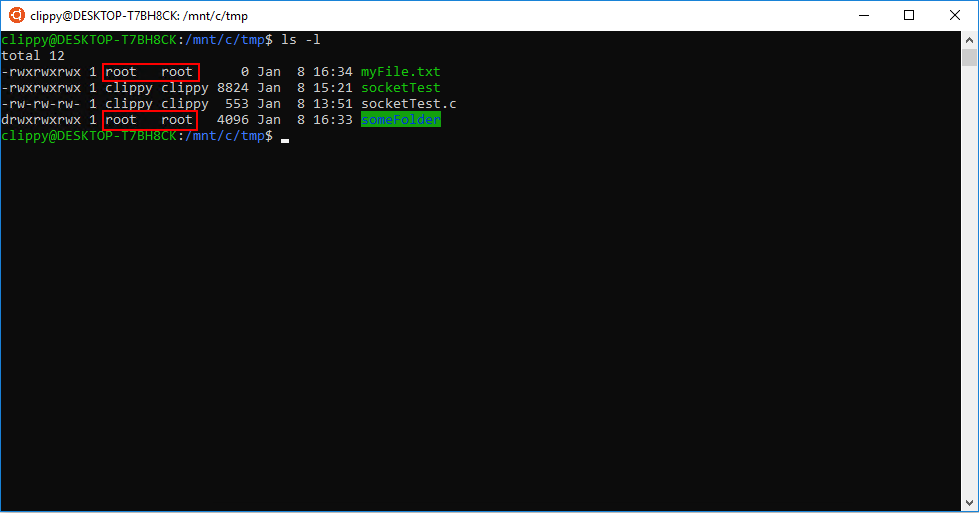



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




The Chmod Command




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



Linux Users And Groups Linode




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
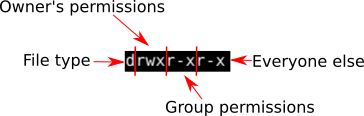



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples




Some Helpful Linux Commands Recently For A Coding Challenge I Was By Kate Schlunz Medium



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively




File Permissions And Chmod Command In Linux Cyber Sophia



What Is Chmod X Command In Linux Linuxtect




Linux Commands Chmod




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Thevoltreport




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




How To Chmod Files Only On Linux




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




In Java How To Set File Permission On A File Using Posixfilepermission Understanding Chmod Command Crunchify




Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux File Permissions Everything You Need To Know Foss Linux



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿